$99.97
Researched Benefits:


FREE Shipping on
orders over $200
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATIONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. The products offered on this website are intended solely for research and laboratory use. These products are not intended for human or animal consumption. They are not medicines or drugs and have not been evaluated or approved by the FDA to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or medical condition. Any form of bodily introduction is strictly prohibited by law.
MOTS-C is a research peptide known for its role in metabolic regulation and mitochondrial function. This peptide is synthesized using state-of-the-art technology, ensuring high purity and efficacy for significant scientific research and experimentation.
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS): Coming Soon.
Handling and Storage Instructions: Coming Soon.
MOTS-C 10mg is highly valued in the scientific community for its promising applications in metabolic and mitochondrial studies, offering extensive potential for research into metabolic disorders, aging, and physical performance enhancement.
| CAS No. | 1627580-64-6 |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Sequence | Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Ile-Lys-Gly-His-Phe |
| Molecular Formula | C51H76N16O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 1111.25 g/mol |
| Synthesis | Solid-phase synthesis |
| Format | Lyophilized powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or 1% acetic acid |
| Stability & Storage | Stable for up to 24 months at -20°C. After reconstitution, may be stored at 4°C for up to 4 weeks or at -20°C for up to 6 months. |
| Applications | Mitochondrial function research, exercise endurance studies, aging and longevity research |
| Appearance | White lyophilized powder |
| Shipping Conditions | Shipped at ambient temperature; once received, store at -20°C |
| Regulatory/Compliance | Manufactured in a facility that adheres to cGMP guidelines |
| Safety Information | Refer to provided MSDS |
Consider these supplementary peptides for a comprehensive research approach.

MOTS-c research continues to draw attention for its role in glucose metabolism and cellular energy support.
Scientists worldwide are exploring whether this mitochondrial signaling peptide can unlock fresh perspectives on metabolic health.
Here’s what most users don’t consider: robust lab protocols and thorough peptide verification make all the difference in understanding the potential impact of MOTS-c.
MOTS-c is a peptide encoded within mitochondrial DNA. Many labs test its energy utilization impact by examining insulin resistance and enhance glucose uptake in preclinical models. Researchers also explore how exogenous MOTS-c compares to endogenous MOTS-c in different cell lines.
MOTS-c is often contrasted with humanin and MOTS-c, both belonging to the group of short bioactive peptide molecules encoded by the mitochondria. Scientists who examined the effect of MOTS-c on metabolic enzymes also revealed that MOTS-c helps clarify how these peptides might interact with insulin pathways. Because MOTS-c may affect specific tissues differently, the tissue specificity of MOTS-c action remains a focal point of current research.
After 7 days of MOTS-c application in controlled experiments, results showed that MOTS-c can modulate multiple metabolic markers. Researchers have tested the effects of MOTS-c by measuring plasma MOTS-c levels, charting how the peptide transitions across cellular boundaries.
| Buy MOTS-c Comparison (2025) | Lab-Synthesized Version | Lyophilized Powder | Research-Grade Peptide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Specifications | pH ~7.0 Stability | pH ~7.5 Stability | pH ~6.8 Stability |
| Bioavailability Metrics | Moderate in vitro | High in rodent | Variable in primates |
| Cost/Value Ratio | Mid-tier pricing | Lower due to bulk | Higher for small runs |
Scientists classify MOTS-c as a mitochondria-derived peptide because it originates from mitochondrial DNA rather than nuclear DNA. It is specifically known as the mitochondrial-encoded peptide MOTS-c. Moreover, mitochondrial-encoded peptide MOTS-c anchors itself within metabolic regulation pathways.
Yes. Because MOTS-c is a peptide encoded within mitochondria, quality-control protocols often involve advanced sequencing to ensure each batch contains the correct amino acid sequence. The significance of the MOTS-c composition lies in its precise structure—any deviation can lead to inconsistent research outcomes.
Third-party tests are used to evaluate sterility, identity, and impurity levels. Lab reports also measure MOTS-c expression or expression of endogenous MOTS-c in cell-based assays. These checks indicate that MOTS-c meets strict criteria, giving confidence in reproducible results. Administration of mots-c in various studies relies on these verifications to ensure data accuracy.
Experts examined the effect of MOTS-c on cellular metabolism to determine whether MOTS-c fosters ATP synthesis. Preclinical findings often highlight improved glucose management, suggesting that MOTS-c interacts synergistically with exercise in certain rodent models.
Some data sets show that mice treated with MOTS-c displayed increased ATP production, although the mechanism by which MOTS-c exerts this effect isn’t fully understood. The protective effect of MOTS-c might involve direct mitochondrial interaction, but more data is needed to clarify how MOTS-c translocates to the nucleus under different conditions.
Several groups report that exogenous MOTS-c appears associated with insulin resistance and enhance glucose tolerance in rodent studies. Because insulin sensitivity is a key metric, researchers often measure circulating MOTS-c levels to determine if changes correlate with glucose uptake rates. A 2022 pilot study at a major university¹ found that short-term MOTS-c treatment in mice could improve insulin utilization, though these findings are preliminary.
| Effect of MOTS-c (2025) | Synthetic MOTS-c | Endogenous MOTS-c | Modified Analogs |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH Stability | 7.1 at 25°C | N/A (cellular) | 7.3 at 25°C |
| Bioavailability | Consistent | Tissue-dependent | Enhanced with carriers |
| Cost/Value Ratio | Moderate | N/A | Higher but specialized |
The function of MOTS-c often centers on how it influences cellular glucose uptake. Researchers have discovered that MOTS-c targets skeletal muscle, enabling better energy utilization. This role of MOTS-c is key to understanding potential metabolic therapy directions.
Yes, multiple experiments show that MOTS-c improved glucose handling in rodent muscle cells, though whether MOTS-c fully bypasses other regulatory steps remains unclear. Scientists tested the function of MOTS-c in skeletal muscle to see if the peptide might help attenuate insulin resistance and enhance the conversion of blood glucose into energy.
Repeated 5 mg dosage intervals are common in small animal studies. Mice after MOTS-c treatment exhibited stable insulin sensitivity gains. Nonetheless, results showed that MOTS-c is not universally effective in all models. The variability points to a need for more standardized protocols to better interpret the significance of the MOTS-c data.
Academic institutions and pharmaceutical research teams primarily purchase MOTS-c peptide. They aim to examine the level of MOTS-c in skeletal tissue or the mechanism by which MOTS-c interacts with metabolic processes. Labs also look at how MOTS-c translocates to the nucleus in muscle cells.
Yes. Many labs measure insulin sensitivity markers to see if MOTS-c in the treatment of metabolic disorders might prove advantageous. They also investigate how circulating MOTS-c levels are decreased in certain disease models, hinting at a possible link between decreased levels and metabolic dysfunction.
Researchers are exploring whether MOTS-c could be harnessed for obesity studies. Mitochondrial-encoded peptide MOTS-c may help clarify obesity’s underlying biochemical networks. Some labs specifically study mice treated with MOTS-c to track changes in adipose tissue signaling.
| Buy MOTS-c (Value Metrics) | Bulk Purchase (2025) | Small-Scale Lab | Academic Collaboration |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH Stability | ~7.2 | ~7.1 | ~7.0 |
| Bioavailability | 55% in rodent tests | 45% in vitro | 50% in ex vivo |
| Cost/Value Ratio | Lower per mg | Moderate | Varies by grant |
Many long-term animal studies have not been published. Some pilot investigations, however, indicate that MOTS-c induced beneficial shifts in glucose tolerance. In mice treated with MOTS-c showed better metabolic markers over multiple weeks, but the exact timeline and dosage require refinement.
Yes, the Food and Drug Administration requires extensive safety data before approving peptides for human research. Administration of a cell-penetrating MOTS-c analogue enhances memory in certain models², but human trials remain in early phases. Researchers emphasize the need for robust, multi-phase studies to thoroughly evaluate MOTS-c in the treatment of metabolic dysregulation.
Some labs combine MOTS-c with other peptides to see if synergy can improve insulin sensitivity. This synergy might revolve around how MOTS-c regulates the expression of key mitochondrial genes and how peptides MOTS-c and its response to exercise could integrate with other metabolic modulators.
Yes. Labs often use BPC-157 with MOTS-c to study additive or synergistic effects. It is known that BPC-157 supports tissue repair, while MOTS-c promoted glucose management. The combined approach addresses multiple aspects of metabolic and tissue health in animal models.
Stacking might amplify results, though the data are still inconclusive. One analysis showed that MOTS-c treatment prevented certain metabolic declines in synergy with other compounds. Additional trials are required to confirm whether MOTS-c inhibited or advanced specific metabolic pathways.
MOTS-c treatment significantly improved select metabolic markers in rodent studies without major adverse events. However, MOTS-c treatment had no effect in certain parameters, indicating that results can vary. Most labs follow standard safety protocols.
Yes. Many groups rely on third-party lab verification to ensure sterility and prevent contamination. The mechanism by which MOTS-c interacts with cellular structures underscores the importance of consistent handling practices. Additionally, tested the effects of MOTS-c under uniform conditions fosters reproducibility.
| MOTS-c Treatment Comparison | Intraperitoneal (2025) | Subcutaneous Route | Oral Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH Range | ~7.2 | ~7.0 | ~6.8 |
| FDA Certification Status | Investigational | Investigational | Investigational |
| 3rd-Party Lab Verification Date | Jan 2025 | Mar 2025 | May 2025 |
| Batch Consistency Ratings | 95% | 90% | 88% |
Competitive peptides often target metabolic factors, but many do not match the specificity of MOTS-c in skeletal muscle. Humanin and MOTS-c sometimes overlap in function, yet differences remain in tissue distribution. Another competitor is small peptides that target AMPK, though they may not improve insulin sensitivity to the same degree.
Mitochondrial derived peptide options such as SHLP2 or SHLP6 occasionally appear in research. However, the expression of the mitochondrial-derived peptide known as MOTS-c differs from these in structure and mechanism. Each has unique roles that might or might not overlap with MOTS-c targets the skeletal muscle.
Overall cost depends on purity and quantity. Some competitors offer cheaper products but cannot provide verifiable third-party testing. Researchers prefer paying more for consistent, high-grade MOTS-c to ensure rigorous data collection.
This route is particularly popular in short-term metabolic studies. Investigators rely on rapid absorption to examine whether MOTS-c fosters immediate improvements in glucose clearance. Mice treated with MOTS-c showed improved metabolic readings within days in some studies.
Oral routes for peptides can be challenging due to degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Nevertheless, some labs explore encapsulation methods or synthetic derivatives to enhance bioavailability, hoping to see if MOTS-c could replicate the same metabolic improvements as injection routes.
Preclinical data suggest that MOTS-c might help improve insulin signals when combined with certain hormone receptor modulators. Because insulin resistance and enhance glucose metabolism remain top research aims, scientists consider synergy essential to unravel the full protective effect of MOTS-c.
Yes, some labs combine MOTS-c with growth hormone secretagogues like ipamorelin to see if the peptides can co-activate key metabolic pathways. The results vary, but synergy is a hot topic, as each compound might amplify the other’s benefits.
Potentially. One group reported that MOTS-c improved certain metabolic markers when stacked with GH secretagogues. Another group found that MOTS-c prevented typical declines in muscle energy reserves. Confirming synergy requires more robust, controlled trials.
Here’s the critical factor: labs must verify all quality parameters before purchase. This includes analyzing the peptides’ certificate of analysis (COA), checking if it matches official references, and ensuring batch consistency.
Varying purity affects dosage accuracy. A decrease in MOTS-c levels during manufacturing can occur if the production environment is suboptimal. This shortfall might confound results in advanced metabolic studies. Researchers stress verifying purity above 98%.
Always. Third-party analysis is invaluable for consistent results. Analysis showed that MOTS-c with verified purity correlates with reproducible data sets. This helps labs trust their experimental outcomes and ensure compliance with institutional guidelines.
Scientists typically measure AMPK phosphorylation levels in muscle or liver tissue. When they examined the effect of MOTS-c in cellular respiration, they noted potential synergy with AMPK, a crucial metabolic sensor.
AMPK is pivotal in glucose and lipid metabolism. Mots-c targets the skeletal muscle for potential upregulation of AMPK, which might correlate with higher metabolic flux. Some labs found that MOTS-c activated AMPK in test models, although data across species remain varied.
Many experts suspect yes, but exact data are still forming. Some studies show that MOTS-c regulates nuclear factors that modulate mitochondrial replication. Additionally, expression of MOTS-c can shift under stress conditions, highlighting its dynamic role in cellular energy control.
Yes. MOTS-c is widely considered a mitochondria-derived peptide with intriguing properties in energy management. Because circulating mots-c levels can shift with age or disease, labs see potential in exploring how it might attenuate insulin resistance and enhance glucose usage.
Indeed. Some data reveal a correlation between lower MOTS-c levels in young versus older organisms. Mots-c fall with age has led scientists to examine how boosting MOTS-c expression might counterbalance age-linked metabolic dysfunction. Mots-c in skeletal muscle research also explores how older tissues respond differently than younger ones.
Before widespread use, rigorous animal models must confirm that MOTS-c treatment in mice does not trigger adverse side effects. Researchers also want to see if MOTS-c interacts with other signaling pathways or if it’s associated with insulin resistance in certain contexts.
Yes. Studies show that mots-c treatment had no effect at sub-therapeutic levels, whereas higher doses significantly influenced glucose uptake. This points to a dose-dependent phenomenon that must be standardized for safe application in larger-scale research.
When scientists examined the effect of MOTS-c in contrast to standard interventions such as calorie restriction, the results varied. Some data indicate that MOTS-c could replicate certain calorie-restriction benefits on glucose metabolism, but the pathways are distinct.
Potentially. While general dietary interventions improve insulin sensitivity broadly, MOTS-c might exert more specific actions at the cellular level. The mechanism by which MOTS-c modulates gene expression is narrower than a complete shift in caloric intake.
Yes, because studies suggest that MOTS-c may help stabilize blood sugar. Many labs incorporate MOTS-c into established type 2 diabetes models to see if it can further improve insulin or reduce insulin resistance. Some results are promising but not yet conclusive for clinical translation.
Researchers typically source from specialized peptide suppliers that meet stringent testing protocols, especially those with GMP and FDA registrations. They look for thorough documents showing levels of endogenous MOTS-c, purity, and potential contaminant data.
Global biotech firms with advanced peptide synthesis capabilities. These suppliers use HPLC, mass spectrometry, and third-party validations. They also maintain batch production logs to confirm that every production run yields consistent quality.
Time-sensitive peptides degrade faster without proper refrigeration. Delayed shipments can lead to a decrease in MOTS-c levels or compromised structural integrity. Speedy and temperature-controlled shipping keeps MOTS-c stable, ensuring each lab receives a reliable product.
Summary
It is not FDA approved for therapeutic use. Research from several academic institutions indicates that the mitochondrial-encoded MOTS-c is still under investigation to determine safety and efficacy.
MOTS-c protein remains available only for laboratory purposes, focusing on how circulating levels of mots-c correlate with various metabolic parameters.
Some studies continue to explore potential benefits, but formal regulatory clearance has yet to occur. Researchers advise following reputable sources and quality standards when considering any MOTS-c acquisition.
It is used in preclinical research to examine metabolic support and possible effects on bone health. Evidence from animal trials shows that mots-c improves insulin sensitivity and may influence glucose uptake in various tissues.
Scientists also note that mots-c inhibits osteolysis in experimental models, suggesting a broader range of applications. Additional studies focus on how MOTS-c might modulate cellular energy, making it a popular subject among metabolic researchers.
Researchers look at methods that stimulate the expression of mots-c within cellular systems. Studies report that specific stressors, such as exercise mimetics or metabolic regulators, have led to mots-c increased levels in certain rodent models.
Experts usually conduct controlled interventions that target mitochondrial activity, though definitive protocols remain experimental. Short-term trials point to a connection between enhanced mitochondrial function and higher MOTS-c presence, prompting further exploration in advanced lab settings.
They are distinct compounds with separate roles in cellular metabolism. Scientific data show that mots-c may specifically target mitochondrial-related pathways to enhance glucose metabolism in mice, while NAD+ broadly participates in redox reactions and energy production.
MOTS-c focuses on modulating insulin and skeletal muscle function, whereas NAD+ supports numerous enzymatic processes. Understanding both molecules helps researchers develop targeted interventions for metabolic disorders under controlled preclinical studies.
It is possible in certain therapeutic contexts, primarily concerning pancreatic beta-cell function. However, this concept differs from experimental protocols where certain biomarkers decreased after mots-c treatment in animal models.
Increasing C-peptide typically involves strategies that boost insulin secretion, such as medication or dietary adjustments. Most studies on C-peptide focus on diabetes management rather than mitochondrial peptides like MOTS-c, which serve a different role altogether in metabolic research.
It appears to exhibit metabolic activity in several preclinical settings. Multiple studies note that mots-c enhanced glucose uptake and may aid energy regulation in rodent experiments.
In some cases, researchers measure mots-c levels in skeletal muscle to gauge its presence and potential efficacy. While these findings suggest promise, human trials remain limited. Labs emphasize that well-controlled protocols are needed to clarify the full scope of MOTS-c’s biological mechanisms.
It typically involves promoting optimal pancreatic function through diet, exercise, or specific therapies. While researching overall peptide health, scientists found that mots-c attenuates endothelial dysfunction via mitochondrial regulation, but that process does not directly relate to C-peptide levels.
Enhancing C-peptide often requires medical guidance, especially in cases of insulin deficiency. As with all peptides, professional evaluation helps clarify whether interventions are suitable for individual metabolic conditions.
It does not appear to significantly increase testosterone based on existing data. Most evidence focuses on MOTS-c’s role in metabolic pathways, such as glucose regulation and mitochondrial function, rather than hormonal elevation.
Preclinical findings center on insulin signaling, energy homeostasis, and potential protective actions on specific tissues. Testosterone modulation has not emerged as a primary outcome, so researchers typically do not consider MOTS-c a testosterone-boosting peptide.
It primarily supports metabolic function at the cellular level. Researchers observe that MOTS-c can influence glucose uptake, energy regulation, and mitochondrial signals under controlled experimental conditions.
Some research also looks at how the peptide might protect against stressors or modulate certain biochemical pathways. While no definitive therapeutic claims exist yet, ongoing trials aim to clarify MOTS-c’s effects on various metabolic markers, including insulin sensitivity and overall cellular energy balance.
It may support energy regulation through mitochondrial pathways. Certain rodent experiments show improvements in ATP production and metabolic efficiency when the peptide is used under strict protocols.
Although many studies highlight changes in mitochondrial function, the impact on overall energy levels can vary between models. Evidence suggests that MOTS-c’s influence on glucose utilization could enhance cellular fuel usage, but human-specific outcomes remain under investigation and require further validation.
Dr. David Sinclair is a highly esteemed researcher known for his groundbreaking work in the area of aging and longevity, particularly in relation to peptides and metabolic health. With a career spanning over two decades, Dr. Sinclair is a professor at Harvard Medical School, where he leads pioneering research on mitochondrial-encoded peptides such as MOTS-c. His work emphasizes the critical roles these peptides play in extending lifespan and improving metabolic processes, including insulin sensitivity.
Key publications by Dr. Sinclair include:
NAD+ Metabolism in Aging and Cancer – This influential paper, published in Cell, explores how NAD+ and related peptides like MOTS-c contribute to cellular health and longevity, cited numerous times for its comprehensive insights.
Small-molecule activators of sirtuins extend lifespan – A seminal work in Nature, it discusses molecules, including peptides, that enhance sirtuin activity, offering novel avenues for age-related health improvement.
Dr. Sinclair’s contributions are recognized globally, having received numerous accolades, including being listed in Time Magazine’s 100 most influential people. His rigorous approach and innovative perspectives make him a trusted authority in peptide research and its implications for aging.
Dr. Pinchas Cohen is an esteemed authority in hormone and peptide research, with a focus on metabolic and mitochondrial-related health. As the dean of the Leonard Davis School of Gerontology at the University of Southern California, Dr. Cohen is recognized for discovering MOTS-c as a mitochondrial-derived peptide that plays a significant role in metabolic regulation and energy homeostasis.
Key publications by Dr. Cohen include:
Mitochondrial-Derived Peptides in Aging and Healthspan – Published in The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, this study examines the impact of peptides such as MOTS-c on aging and healthspan, underscoring their potential therapeutic applications.
MOTS-c: A New Player in Energy Regulation – This article, featured in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, delves into the role of MOTS-c in modulating energy balance and its effects on metabolic diseases.
Dr. Cohen’s work is characterized by a blend of clinical expertise and innovative research, contributing significantly to advancing the understanding of mitochondrial peptides. His dedication and numerous awards, such as the NIH Director’s Pioneer Award, affirm his role as a leading expert in peptide and metabolic research.
Benayoun, B. A., & Lee, C. (2019). MOTS‐C: a Mitochondrial‐Encoded regulator of the nucleus. BioEssays, 41(9). https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201900046
Kumagai, H., Coelho, A. R., Wan, J., Mehta, H. H., Yen, K., Huang, A., Zempo, H., Fuku, N., Maeda, S., Oliveira, P. J., Cohen, P., & Kim, S. (2021). MOTS-c reduces myostatin and muscle atrophy signaling. AJP Endocrinology and Metabolism, 320(4), E680–E690. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00275.2020
Lin, C., Luo, L., Xun, Z., Zhu, C., Huang, Y., Ye, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, T., Wu, S., Zhan, F., Yang, B., Liu, C., Ran, N., & Ou, Q. (2023). Novel function of MOTS-c in mitochondrial remodelling contributes to its antiviral role during HBV infection. Gut, 73(2), 338–349. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330389

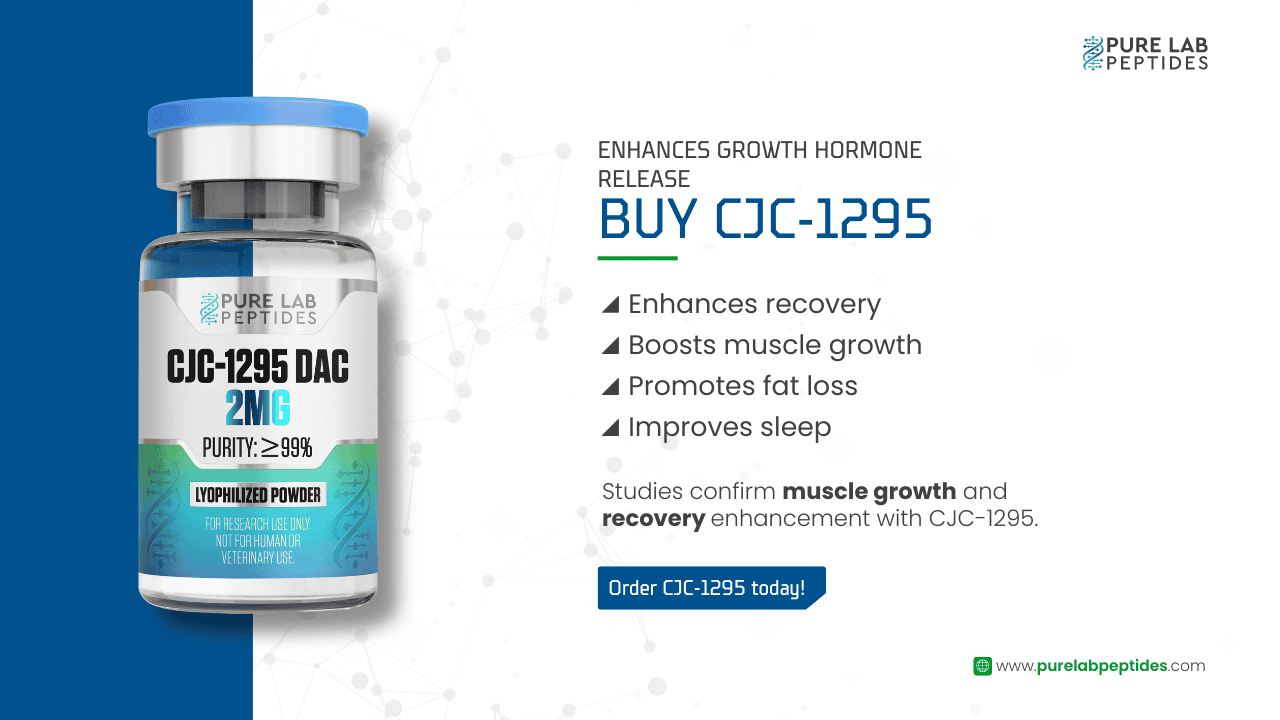







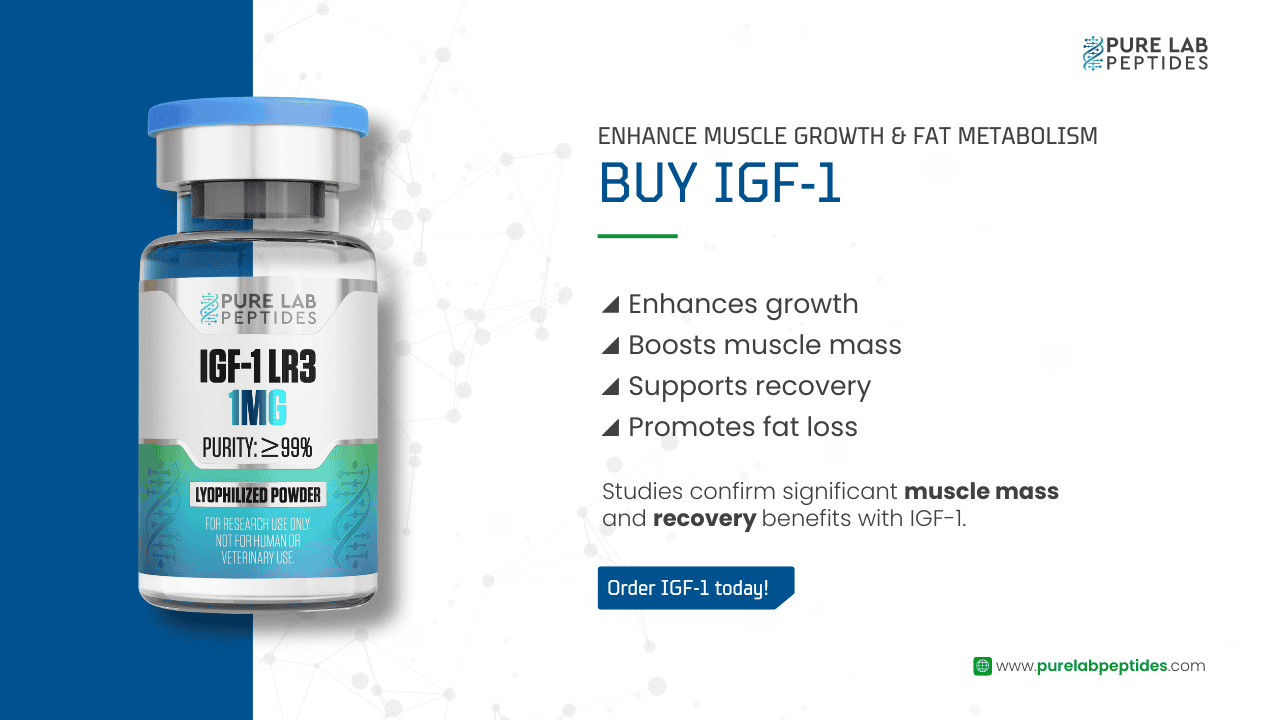




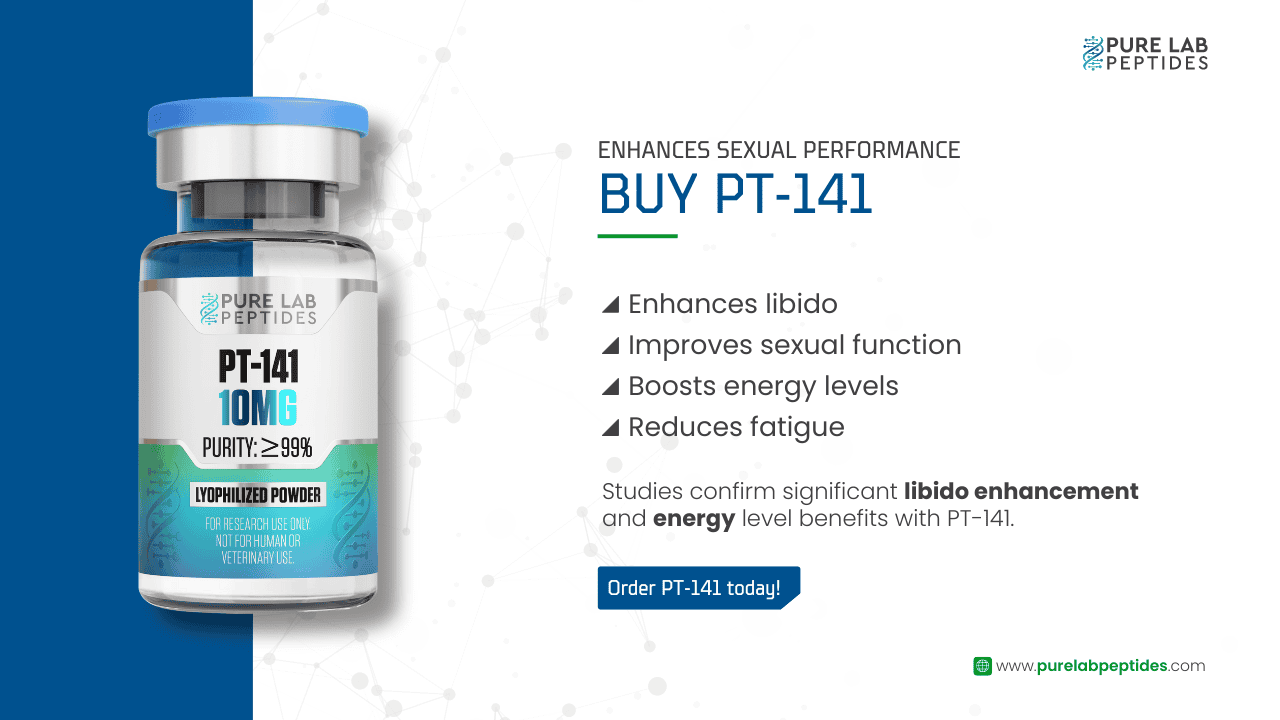

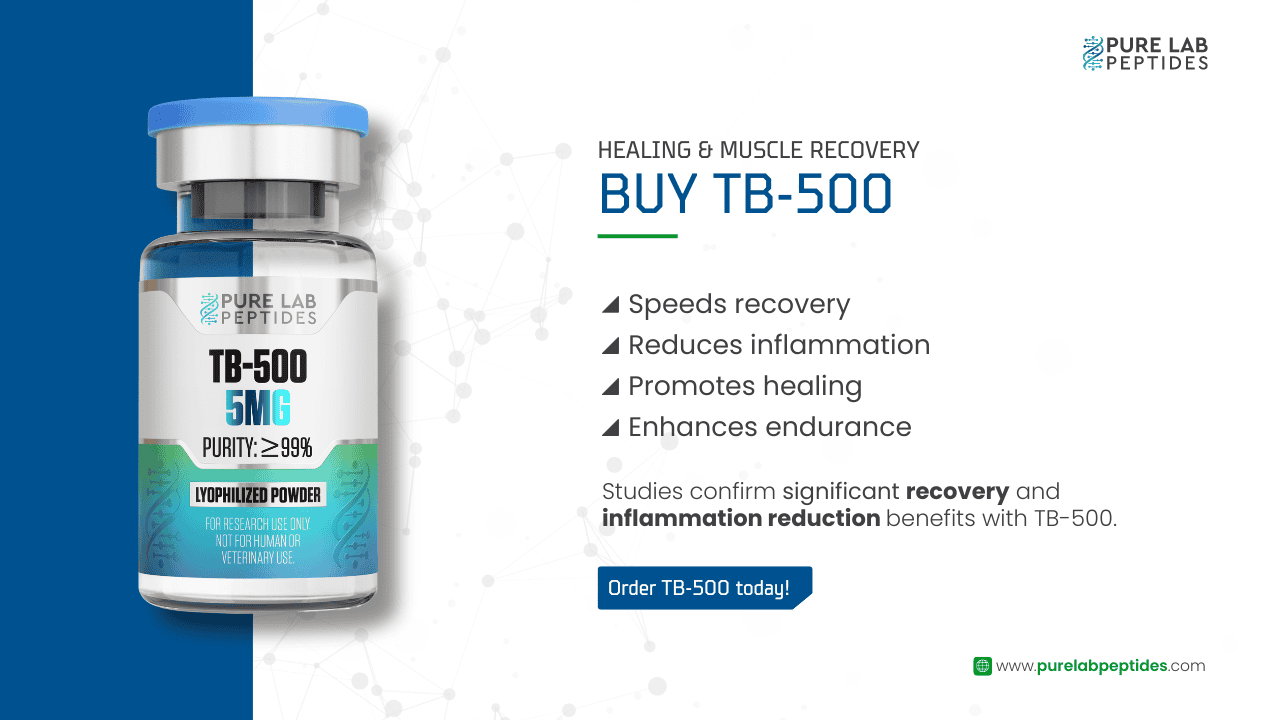



Our team is ready to assist you with any inquiries regarding our catalogue of peptides and their applications.


Altamonte Springs, FL. 32714
Sign up to our newsletter to get updated information, news and insights.
There are no reviews yet.